What is Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a helpful and powerful program for data analysis and documentation. It is a spreadsheet program, which contains a number of columns and rows, where each intersection of a column and a row is a “cell.” Each cell contains one point of data or one piece of information. By organizing the information in this way, you can make information easier to find, and automatically draw information from changing data.
The Excel Interface
File Tab & Ribbon
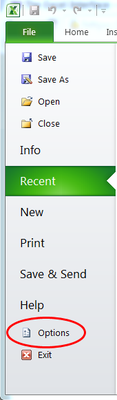
In Excel 2010, the Office button ![]() has been replaced by a modification of the familiar File menu
has been replaced by a modification of the familiar File menu ![]() . Click to reveal the New, Open, Save, Print and Close options.
. Click to reveal the New, Open, Save, Print and Close options.
If you are upgrading to 2010 from 2007, not much of the interface has changed. However, if you are upgrading from an older version of Excel, you may be unfamiliar with the new interface, which will be explained in the sections below. Seven tabs are displayed across the top-left of the window. When you select a tab, a number of options will be displayed as buttons with text labels and picture icons for easy identification. The tabs and their options are known as the Ribbon. The options are organized under the tabs in groups of related features. You can expand the groups by clicking the arrow ![]() in the right of the group box.
in the right of the group box.
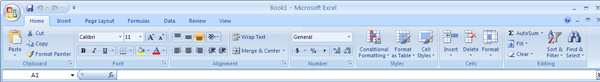
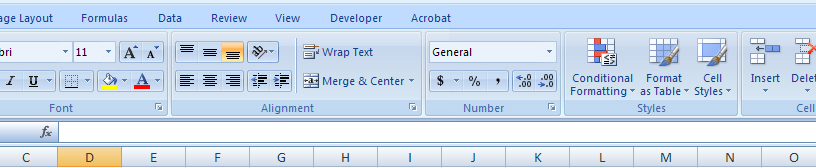
Home Tab
The Home tab contains the most common text editing tools used in Excel.
The most common Excel commands and functions can be accessed quickly by using the shortcut menu. To access this feature, simply right-click the element you wish to edit if you are using a PC, or control-click the element you wish to edit if you are using a Mac. The options displayed will vary depending on the element you have selected.
Spreadsheet Basics
Each Excel file is a workbook that can hold many worksheets. The worksheet is a grid of columns (designated by letters) and rows (designated by numbers). The letters of the columns are indicated in the blue buttons across the top of the worksheet. The numbers of the rows are indicated in the blue buttons down the left of the worksheet. The intersection of a column and a row is called a cell. You can input your data into the cells. Cells can contain text, numbers, or formulas for automatic calculations. Each cell on the spreadsheet has a cell address that is the column letter followed by the row number.
Formula bar
This will be one of the most useful tools as you use Excel. The formula bar allows you to see all the details and methods used to return what is seen in a cell. Whenever you input any information into a cell, the output, or end result is what is shown once you move away from the cell. This is most prominent when using functions, as you do not see the whole equation in the cell in the worksheet, only the result. The formula bar is located below the ribbon and spans most of the window.
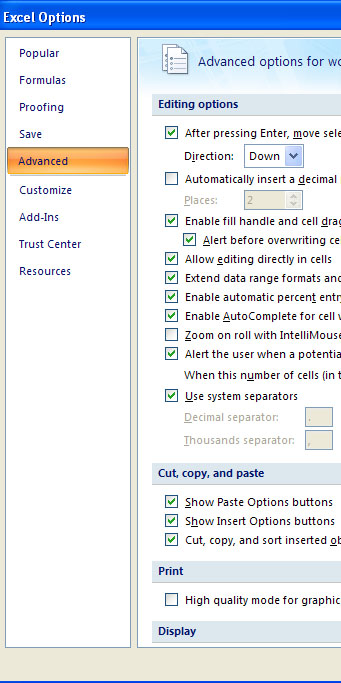
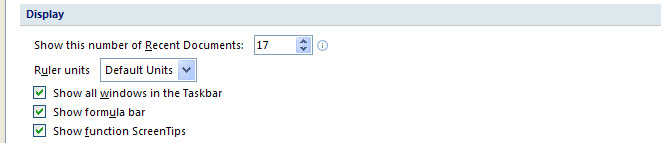
It is possible to hide the formula bar, though is not recommended. In order to hide or show the formula bar if it has mistakenly been hidden, go to Excel Options at the bottom right of the menu that opens when you click the Office button. Go to the Advanced option, and under Display, you can click the check box for Show formula bar. When done, simply click Ok.
 |  | |
 | ||
Adding a Worksheet
By default, three worksheets are included in each Excel workbook. You can access the different worksheets by clicking the worksheet tabs just above the status bar.
To add a new worksheet, click the Insert Worksheet tab, to the right of the existing worksheet tabs.
Renaming a Worksheet
To rename a worksheet tab, follow either of these steps:
- StepsActions
- Option 1
- Right-click the tab you want to rename if you are using a PC, or control-click the tab you want to rename if you are using a Mac. A shortcut menu will open.
- Click Rename from the shortcut menu.
- Type the new name.
- Press .
- Option 2
- Hover over the tab you want to rename, and double Left-click the tab.
- Begin typing to rename the tab.
- Press .
Basics
This section explains the basics of Excel.
1 Ribbon: Excel selects the ribbon's Home tab when you open it. Learn how to use the ribbon.
2 Workbook: A workbook is another word for your Excel file. When you start Excel, click Blank workbook to create an Excel workbook from scratch.
3 Worksheets: A worksheet is a collection of cells where you keep and manipulate the data. Each Excel workbook can contain multiple worksheets.
4 Format Cells: When we format cells in Excel, we change the appearance of a number without changing the number itself.
5 Find & Select: Learn how to use Excel's Find, Replace and Go To Special feature.
6 Templates: Instead of creating an Excel workbook from scratch, you can create a workbook based on a template. There are many free templates available, waiting to be used.
7 Data Validation: Use data validation in Excel to make sure that users enter certain values into a cell.
8 Keyboard Shortcuts: Keyboard shortcuts allow you to do things with your keyboard instead of your mouse to increase your speed.
9 Print: This chapter teaches you how to print a worksheet and how to change some important print settings in Excel.
10 Share: Learn how to share Excel data with Word documents and other files.
11 Protect: Encrypt an Excel file with a password so that it requires a password to open it.




No comments:
Post a Comment